In [1]:
1
2
3
4
5
import sys, random, time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
sys.path.append("/home/swyoo/algorithm")
from utils.verbose import logging_time, printProgressBar
we should expand recursion limitation. refer how to expand it in geeksforgeeks
In [2]:
1
# sys.setrecursionlimit(10**7)
chap 4
find maximum - subarray problem
-
Brutal Force sol :$Ω(n^2)$ 이고, $O(n^3)$
-
Better sol :$O(n^2)$
-
Divide and Conquer
[idea]
- max subarray lies among 3 cases : 1. left: A[low..mid] 2. right: A[mid+1..high] 3. cross: A[mid..high]
- $T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n = O(nlgn)$
-
Linear time algorithm
In [3]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 1. brutal force
@logging_time
def find_maximum_subarray0(A):
n = len(A)
MaxSum = 0
for i in range(n): # 처음위치 i 선택
for j in range(i,n): # 끝 위치 j 선택
ThisSum = 0
for k in range(i,j+1): # A[i..j] 까지의 합
ThisSum = ThisSum + A[k]
if ThisSum > MaxSum: # Max 값을 찾으면 update
MaxSum = ThisSum
return MaxSum
# 2. better brutal force
@logging_time
def find_maximum_subarray1(A):
n = len(A)
MaxSum = 0
for i in range(n): # 처음위치 i 선택
ThisSum = 0
for j in range(i,n): # A[i..j] 까지의 합
ThisSum = ThisSum + A[j]
if ThisSum > MaxSum: # Max 값을 찾으면 update
MaxSum = ThisSum
return MaxSum
In [4]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# 3. divide and conquer method
def find_max_crossing_subarray(A, low, mid, high):
max_left = low # initial value 존재 해야한다. local variable을 output으로 할 수 없음
max_right = low
left_sum = -float('inf')
loc = 0
for i in range(mid , low - 1, -1):
loc += A[i]
if loc > left_sum:
left_sum = loc
max_left = i
right_sum = -float('inf')
loc = 0
for j in range(mid+1, high + 1):
loc = loc + A[j]
if loc > right_sum:
right_sum = loc
max_right = j
return max_left, max_right, left_sum + right_sum
@logging_time
def find_maximum_subarray2(A):
def recursion(A, low, high):
if high == low:
return low, high, max(A[low], 0) # base case: only one element
mid = (low + high)// 2
# dividing: T(n/2) + T(n/2)
left_low, left_high, left_sum = recursion(A, low, mid)
right_low, right_high, right_sum = recursion(A, mid+1, high)
# crossing computing: O(n)
cross_low, cross_high, cross_sum = find_max_crossing_subarray(A, low, mid, high)
# decision: O(1)
if left_sum >= right_sum and left_sum >= cross_sum:
return left_low, left_high, left_sum
if right_sum >= left_sum and right_sum >= cross_sum:
return right_low, right_high, right_sum
return cross_low, cross_high, cross_sum
left, right, ans = recursion(A, 0, len(A) - 1)
return ans
In [5]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 4. linear time algorithm
@logging_time
def find_maximum_subarray3(A):
n = len(A)
MaxSum = 0
ThisSum = 0
for j in range(n): # 처음위치 i 선택
ThisSum = ThisSum + A[j]
if ThisSum > MaxSum: # Max 값을 찾으면 update
MaxSum = ThisSum
elif ThisSum < 0:
ThisSum = 0
return MaxSum
In [6]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 5. recursive version linear time algorithm
loc = 0
res = 0
@logging_time
def find_maximum_subarray4(A):
global loc, res
def recursion(i):
""" find maximum subarray of A[:i]. """
global loc, res
if i == 0:
loc = res = max(A[0], 0)
return res
res = recursion(i - 1)
loc += A[i]
res = max(res,loc)
if loc < 0:
loc = 0
return res
return recursion(len(A) - 1)
In [7]:
1
2
3
4
5
# functions = [find_maximum_subarray0,
# find_maximum_subarray1,
# find_maximum_subarray2,
# find_maximum_subarray3,
# find_maximum_subarray4]
In [8]:
1
2
3
4
functions = [find_maximum_subarray0,
find_maximum_subarray1,
find_maximum_subarray2,
find_maximum_subarray3]
time limit을 두고, 시간이 너무 오래걸리면 flag를 설정하여 더이상 실험하지 않도록 한다.
In [9]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
num_func = len(functions)
num_exp = 20
nrange = 100 # range of numbers.
m_ratio = [0.2, 0.4, 0.6] # negative rate.
num_ratio = len(m_ratio)
t = [[[num_exp]*num_exp for j in range(num_func)] for _ in range(num_ratio)]
breaks = [[-1]*num_func for _ in range(num_ratio)]
sizes = list(np.logspace(start=0, stop=7, num=num_exp))
for k, ratio in enumerate(m_ratio):
print("start ratio {} experiments{:<100}".format(ratio,""))
exp = [True] * num_func
ans = [-1] * num_func
start = time.time()
for i, size in enumerate(sizes):
size = int(size)
A = [random.randint(int(- ratio * nrange), int((1 - ratio) * nrange)) for _ in range(size)]
for j in range(num_func):
if exp[j]: ans[j], t[k][j][i] = functions[j](A)
else: t[k][j][i] = t[k][j][i-1]
if exp[j] and t[k][j][i] > 1000:
exp[j] = False
breaks[k][j] = i + 1
print("exp[{}] exceeds 1 second. ".format(j))
# sanity check
answers = [ans[j] for j, e in enumerate(exp) if e == True]
assert all(e == answers[0] for e in answers), "{}|{}".format(A, answers)
printProgressBar(iteration=i + 1,
total=num_exp,
msg="{}/{}, size {} end| elapsed: {:.2f} ms".format(i + 1, num_exp, size, (time.time() - start) * 1e3),
length=50)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
start ratio 0.2 experiments
exp[0] exceeds 1 second. --------------------------| 40.0 % - 8/20, size 379 end| elapsed: 466.31 ms
exp[1] exceeds 1 second. ███-----------------------| 55.0 % - 11/20, size 4832 end| elapsed: 7120.32 ms
exp[2] exceeds 1 second. ████████████████----------| 80.0 % - 16/20, size 335981 end| elapsed: 13484.50 ms
start ratio 0.4 experiments
exp[0] exceeds 1 second. --------------------------| 40.0 % - 8/20, size 379 end| elapsed: 487.40 ms
exp[1] exceeds 1 second. ███-----------------------| 55.0 % - 11/20, size 4832 end| elapsed: 7208.18 ms
exp[2] exceeds 1 second. ████████████████----------| 80.0 % - 16/20, size 335981 end| elapsed: 13623.80 ms
start ratio 0.6 experiments
exp[0] exceeds 1 second. --------------------------| 40.0 % - 8/20, size 379 end| elapsed: 534.79 ms
exp[1] exceeds 1 second. ███-----------------------| 55.0 % - 11/20, size 4832 end| elapsed: 7562.51 ms
exp[2] exceeds 1 second. ████████████████----------| 80.0 % - 16/20, size 335981 end| elapsed: 13957.04 ms
|██████████████████████████████████████████████████| 100.0 % - 20/20, size 10000000 end| elapsed: 36646.36 ms
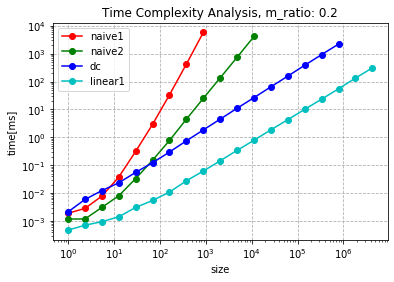
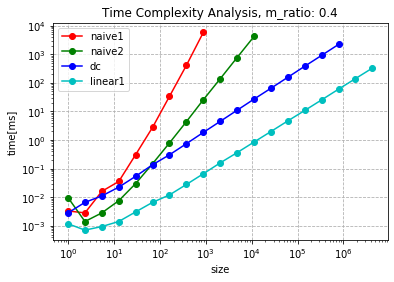
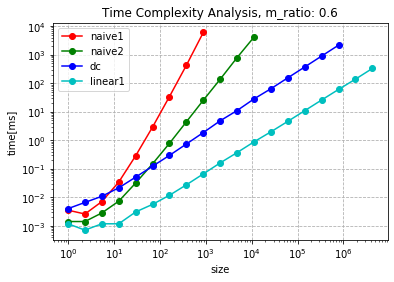
x 축을 log scale로 그리면 한번에 그릴 수있다.
In [10]:
1
breaks
1
[[9, 12, 17, -1], [9, 12, 17, -1], [9, 12, 17, -1]]
In [14]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
for k, ratio in enumerate(m_ratio):
plt.grid(linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('size')
plt.ylabel('time[ms]')
plt.title("Time Complexity Analysis, m_ratio: {}".format(ratio))
s, e = 0, num_exp
plt.xscale('log')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.plot(sizes[s:breaks[k][0]], t[k][0][s:breaks[k][0]], 'o-r', label="naive1")
plt.plot(sizes[s:breaks[k][1]], t[k][1][s:breaks[k][1]], 'o-g', label='naive2')
plt.plot(sizes[s:breaks[k][2]], t[k][2][s:breaks[k][2]], 'o-b', label='dc')
plt.plot(sizes[s:breaks[k][3]], t[k][3][s:breaks[k][3]], 'o-c', label='linear1')
# plt.plot(sizes[s:e], t[k][4][s:e], 'o-brown', label='linear2')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()


Leave a comment