Suppose that $n$ be len(strs), $M$ be a maxium string of strs.
There are three ways to solve this problem.
- Linear Search: $O(nM)$
- Divide and Conquer: $O(nM)$ GeeksforGeeks
- Binary Search: $O(nMlogM)$ GeeksforGeeks
1
2
3
4
# toy examples
M = 6 # len of longest string
strs1 = ["flowers", "flow", "flights"]
strs2 = ["dog", "racecar", "car"]
Linear Search
find LCP = str[0][:i], seaching through str[j] linearly.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
def LCP_linear(strs):
# base cases
if len(strs) == 0:
return ""
if len(strs) == 1:
return strs[0]
# linear scan to find Longest Common Prefix
# initialization
tmp = strs[0]
for j in range(1, len(strs)):
# finish is the length of possible maximum LCP
# tmp be possible maximum LCP
finish = min(len(tmp), len(strs[j]))
tmp = strs[0][:finish]
# search to find LCP precisely
for i in range(finish):
if tmp[i] != strs[j][i]:
tmp = strs[0][:i]
break
return tmp
1
2
print("ex1: ", LCP_linear(strs1))
print("ex2: ", LCP_linear(strs2))
1
2
3
ex1: fl
ex2:
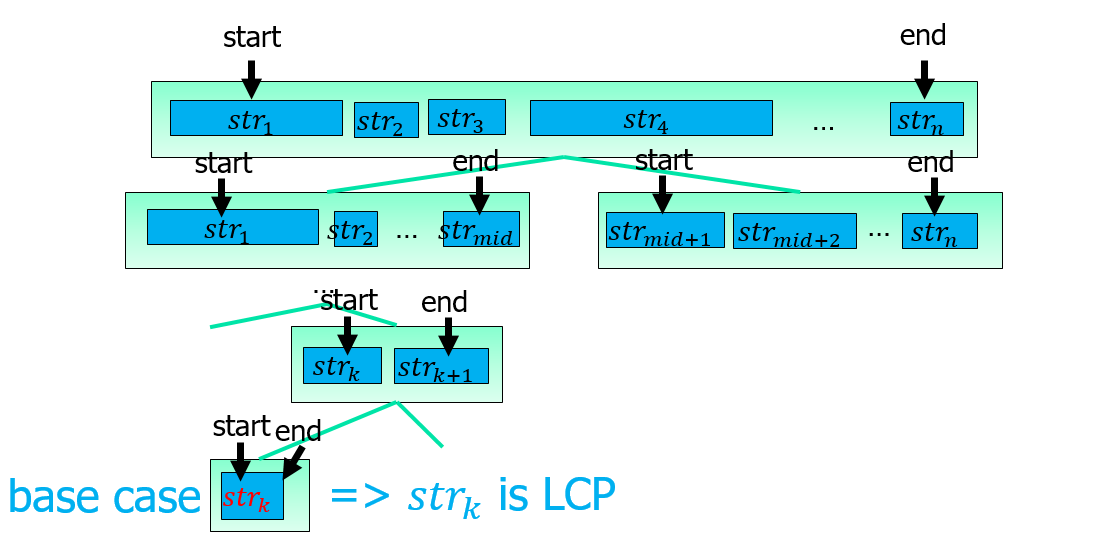
Divide and Conquer
- find left part and right part of LCP.
- find LCP between left part and right part.
key idea is described as follows.
Time complexity analysis
\(\begin{align} T(n) &= 2T(n/2) + M \\ &= 2(2T(n/2^2) + M) + M \\ &= 2^k(T(n/2^k) + (1 + 2 + ... + 2^{k-1})M \\ &= 2^k(T(n/2^k) + (2^{k} - 1)M \\ &= n(T(1) + (n - 1)M \\ &= O(nM) \\ \end{align}\)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# O(M)
def Util(s1, s2):
""" find LCP between s1 and s2. """
finish = min(len(s1), len(s2))
tmp = s1[:finish]
for i in range(finish):
if s1[i] != s2[i]:
tmp = s1[:i]
break
return tmp
def LCP(strs, p, r):
if len(strs) == 0:
return ""
if p >= r:
return strs[p]
mid = (p + r)//2
s1 = LCP(strs, p, mid)
s2 = LCP(strs, mid + 1, r)
return Util(s1, s2)
1
2
print("ex1: ", LCP(strs1, 0, len(strs1)-1))
print("ex2: ", LCP(strs2, 0, len(strs2)-1))
1
2
3
ex1: fl
ex2:
Binary Search
- select the smallest word (to void index overflow, which has length $M$), let it be
loc, in example,geek - let
mid = (s + e)//2, where s, e are start, last index for each. call(s, mid)and in there, check all words to match them withloc[s..mid]to find LCP.- if check returns
True, appendloc[s..e]toans, andcall(mid + 1, e). go to second step. - else, call
call(s, mid - 1)in order to resetans. go to second step.
- if check returns
In this way, we call only left-half or right-helf recursion by checking process, which is a binary search technique.
Note that checking process takes $O(nM)$.
Recursive formula as follows.
\(T(M) = T(M/2) + O(nM) = O(nMlogM)\)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
def solve(strs):
def check(base, s, e):
""" """
for i in range(len(strs)):
j = s
while j <= e and base[j] == strs[i][j]: j += 1
if j != e + 1: return False
return True
def findLCP(loc, s, e):
if s > e: return ""
if s == e:
return loc[s] if check(loc, s, e) else ""
mid = (s + e) // 2
if check(loc, s, mid):
return loc[s:mid+1] + findLCP(loc, mid+1, e)
else:
return findLCP(loc, s, mid-1)
m = len(strs[0]) # length of the shortest word.
loc = strs[0]
for _ in range(len(strs)):
if m > len(strs[_]):
m = len(strs[_])
loc = strs[_]
return findLCP(loc, 0, m - 1)
1
2
strs = ["geeksforgeeks", "geeks", "geek", "geezer"]
solve(strs)
1
'gee'
However, it is too slow, and overhead makes time limited when submitted.
Therefore, iterative solution as follows to avoid overhead(it can be passed in leetcode).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
class Solution(object):
def findMinLength(self, strList):
m = len(strList[0])
for st in strList:
m = min(m, len(st))
return m
def allContainsPrefix(self, strList, str, start, end):
for i in range(0, len(strList)):
word = strList[i]
for j in range(start, end + 1):
if word[j] != str[j]:
return False
return True
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strList):
if len(strList) == 0: return ""
index = self.findMinLength(strList)
prefix = "" # Our resultant string
# We will do an in-place binary search
# on the first string of the array
# in the range 0 to index
low, high = 0, index - 1
while low <= high:
# Same as (low + high)/2, but avoids
# overflow for large low and high
mid = int(low + (high - low) / 2)
if self.allContainsPrefix(strList, strList[0], low, mid):
# If all the strings in the input array
# contains this prefix then append this
# substring to our answer
prefix = prefix + strList[0][low:mid + 1]
# And then go for the right part
low = mid + 1
else:
# Go for the left part
high = mid - 1
return prefix
sol = Solution()
1
2
strs = ["geeksforgeeks", "geeks", "geek", "geezer"]
sol.longestCommonPrefix(strList=strs)
1
'gee'



Leave a comment