1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/swyoo/algorithm/")
import random
from copy import deepcopy
from utils.verbose import logging_time
size = 3
a = list(range(size))
a
1
[0, 1, 2]
Permutation
Recursive Approach
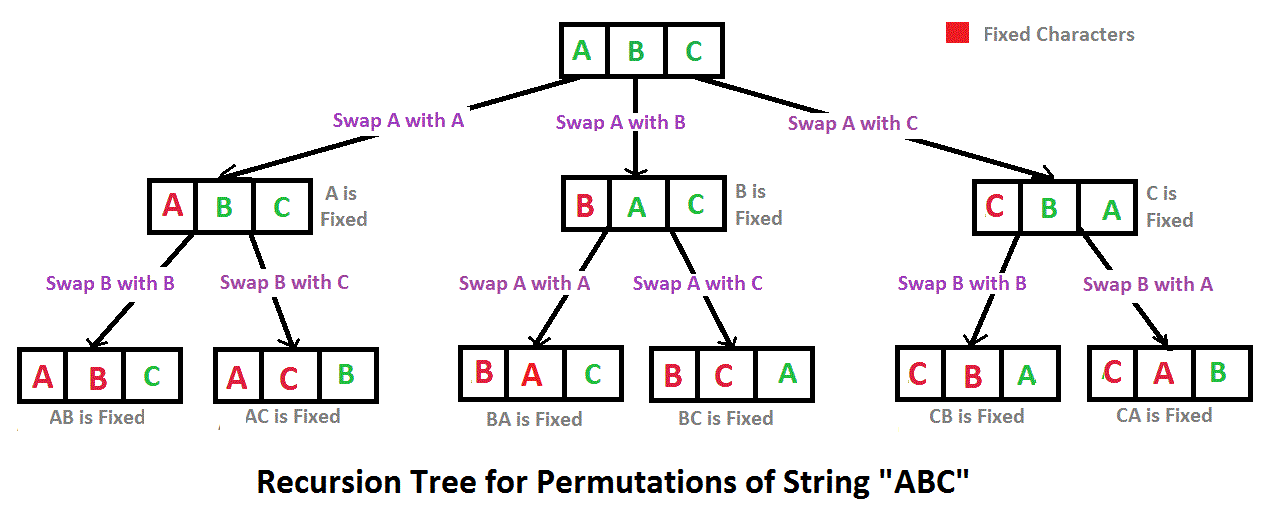
The time complexity is $O(nn!)$
Note that there are $n!$ permutations and it requires $O(n)$ time to print a a permutation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
@logging_time
def solution1(a):
perms = []
def f(s, e):
if s == e:
perms.append(deepcopy(a))
for i in range(s, e + 1):
a[i], a[s] = a[s], a[i]
f(s + 1, e)
a[i], a[s] = a[s], a[i]
f(0, len(a) - 1)
return perms
solution1(deepcopy(a), verbose=True)
1
2
WorkingTime[solution1]: 0.02956 ms
1
[[0, 1, 2], [0, 2, 1], [1, 0, 2], [1, 2, 0], [2, 1, 0], [2, 0, 1]]
Heap’s Algorithm
The time complexity of this algorithm is $O(n!)$.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@logging_time
def solution2(a):
perms = []
def f(size):
if size == 1:
perms.append(deepcopy(a))
return
for i in range(size):
f(size - 1)
if size & 1: # odd
a[0], a[size - 1] = a[size - 1], a[0]
else:
a[i], a[size - 1] = a[size - 1], a[i]
f(len(a))
return perms
solution2(deepcopy(a), verbose=True)
1
2
WorkingTime[solution2]: 0.02432 ms
1
[[0, 1, 2], [1, 0, 2], [2, 0, 1], [0, 2, 1], [1, 2, 0], [2, 1, 0]]
1
2
3
4
size = 9
a = list(range(size))
ans1 = solution1(deepcopy(a), verbose=True)
ans2 = solution2(deepcopy(a), verbose=True)
1
2
3
WorkingTime[solution1]: 2472.30506 ms
WorkingTime[solution2]: 2236.54580 ms
Library
itertools library provides us to get permutations easily.
1
2
3
from itertools import permutations
list(permutations(range(3), 2))
1
[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1)]
Reference
[1] Korean Minusi’s blog
[2] Naive Permutation - geeksforgeeks
[3] Heap’s Algorithm - geeksforgeeks
[4] Permutation with Duplicates - geeksforgeeks


Leave a comment