Two Problems to make use of Disjoint Set(or Union Find)
1
2
3
4
5
from typing import List
from collections import defaultdict
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from networkx.drawing.nx_pylab import draw_networkx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def visualize(par):
""" visualize disjoint set data structure.
:param: par: dictionary, which contains hierachical information of the disjoint set. """
adj = defaultdict(list)
edges = []
for k, v in par.items():
adj[k].append(v)
edges.append((k, v))
g = nx.DiGraph()
g.add_edges_from(edges)
# pos = nx.circular_layout(g)
pos = nx.spring_layout(g, k=0.5, scale=10)
draw_networkx(g, pos=pos, with_labels=True, width=2.0, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
959. Regions Cut By Slashes
I refered Youtube solution.
Given the size of $n \times n$ grid, the time complexity as follows.
(where $\alpha $ is the Inverse-Ackermann function.)
\(O(n^2\alpha)\)
The reasion is that
Disjoint datastructure is built in $O(N\alpha)$, where $N$ is the number of all nodes.
In this problem, the number of all nodes $N$ is $n^2$.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
class Solution:
def regionsBySlashes(self, grid: List[str], show=False) -> int:
par, rnk = {}, {}
def find(x):
if x not in par:
par[x] = x
rnk[x] = 0
return x
if x != par[x]:
par[x] = find(par[x])
return par[x]
def union(x, y):
x, y = find(x), find(y)
if x == y: return
if rnk[x] > rnk[y]:
x, y = y, x
par[x] = y
if rnk[x] == rnk[y]:
rnk[y] += 1
n = len(grid[0])
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, c in enumerate(row):
root = 4 * (i * n + j)
if c != "/":
union(root, root + 2)
union(root + 1, root + 3)
if c != "\\":
union(root, root + 1)
union(root + 2, root + 3)
if i < n - 1:
union(root + 3, root + 4 * n)
if i > 0:
union(root, root - 4 * n + 3)
if j < n - 1:
union(root + 2, root + 4 + 1)
if j > 0:
union(root + 1, root - 4 + 2)
# count representatives
ans = 0
for x in range(4 * n * n):
if x == find(x):
ans += 1
if show:
visualize(par)
return ans
sol = Solution()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
grid = \
[
"/\\",
"\\/"
]
sol = Solution()
ans = sol.regionsBySlashes(grid, show=True)
print("ans: ", ans)
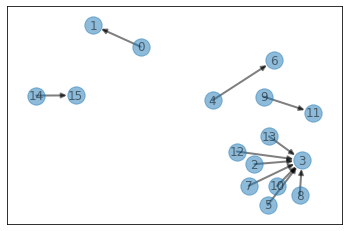
1
2
ans: 5
547. Friend Circles
Easy problem, which is similar with the first problem in leetcode
Given an array M, which means the information of friendship, where the size is $n$
such that
M[i][i] = 1for all students.Mis symmetric
Union Find
Time complexity \(O(n^2\alpha)\)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
class Solution1:
def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]], show=False) -> int:
par, rnk = {}, {}
def find(x):
if x not in par:
par[x] = x
rnk[x] = 0
return x
if x != par[x]:
par[x] = find(par[x])
return par[x]
def union(x, y):
x, y = find(x), find(y)
if x == y: return
if rnk[x] > rnk[y]:
x, y = y, x
par[x] = y
if rnk[x] == rnk[y]:
rnk[y] += 1
n = len(M[0])
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i, n):
if M[i][j]:
union(i, j)
if show:
visualize(par)
ans = 0
for x in range(n):
if x == find(x):
ans += 1
return ans
sol1 = Solution1()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
""" generate an grid. """
import numpy as np
n = 32
rate = 0.96 # density of 0
tmp = np.random.choice(a=[False, True], size=(n, n), p=[rate, 1 - rate]).astype(int)
tmp = np.tril(tmp) + np.tril(tmp, -1).T
grid = (np.identity(n, dtype=bool).astype(int) | tmp).tolist()
# grid = \
# [[1,1,0],
# [1,1,0],
# [0,0,1]]
1
2
3
sol1 = Solution1()
ans1 = sol1.findCircleNum(grid, show=True)
ans1
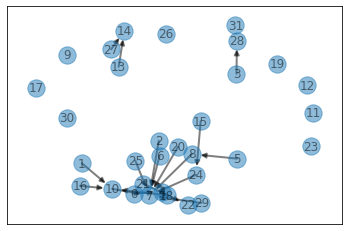
1
13
DFS
Idea:
- mark visted people by searching the friendship matrix.
- count starting
dfs. \(O(n^2)\) This is because the algortihm sees each element only once.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution2:
def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(M[0])
seen = set()
def dfs(start):
seen.add(start)
for j, direct in enumerate(M[start]):
if direct and j not in seen:
dfs(j)
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
if i not in seen:
dfs(i)
ans += 1
return ans
sol2 = Solution2()
1
2
ans2 = sol2.findCircleNum(grid)
ans2
1
13
1
assert ans1 == ans2


Leave a comment