Relay Policy Learning
RPL 논문 을 번역하며 요약해보았다.
Introduction
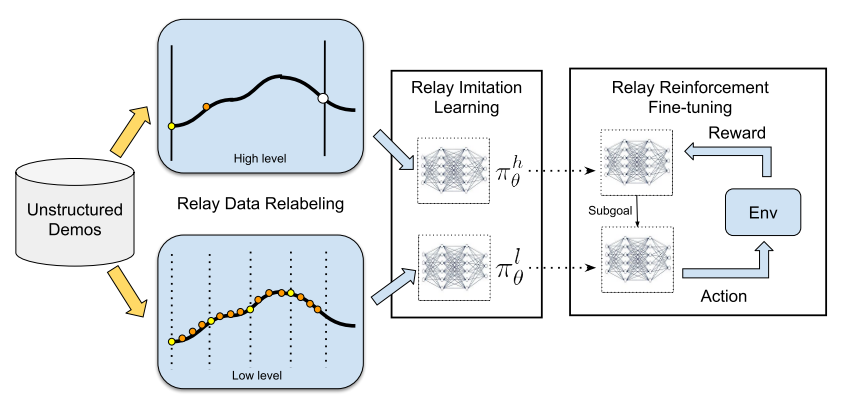
multi-stage, long-horizon robotic tasks 를 해결하기 위한 Relay policy Learning (RPL) 방법을 제안했고 2 phase로 되어있다.
Goal conditioned hierarchical policy를 생성하는 Relay Imitation Learning(RIL) stage
생성된 Policy를 fine tuning 하는 Relay Reinforcement Fine tuning(RRF) stage
기존의HRL은 temporal abstraction을 도입하므로써 long-horizon problem을 풀 수 잇는 실마리를 제공했다. 하지만 아래와 같은 practical한 challenge가 있었다.
Exploration
Skill segmentation
Reward definition
그래서 unstructured human demonstration 의 형태로 extra supervision 을 활용하여 위의 문제를 풀고자 했다.
그래서 생각해낸 접근 방법이 Hierarchical Imitation Learning(HIL) 이다. 그 접근 방법의 목표는 두가지가 있었다.
Temporal task abstraction을 학습하는 것
demonstration에서 의미있는 sub task들을 발견하는 것
기존 방법과 다른점
HRL 방법과 다른점은 unstructured demonstration의 이점을 활용한다. 즉 완벽한 subtask segmentation에 초점을 맞추는 것이 아닌 goal conditioned policy를 fine tuning하여 HRL에서 challenging했던 long-horizon task에 amenable하도록 하는 것을 말한다. 이점은 아래와 같다.
Generalization
Subtask design의 부담을 줄임
RRF를 도움
첫번째 이유는 data가 unsegmented, unstructured, undifferentiated 이든지 간에 어떤 demonstration data든지 적용가능하기 때문이다. 두번째 이유는 segmentation 혹은 subgoal에 대한 정의의 explicit한 형태를 요구하지 않기 때문이다. 세번째 이유는 모든 low level의(subgoal에 대한) trajectory들이 goal-conditioned 되어있고 제한된 같은 길이이기 때문에 RRF과 연속적인 policy의 개선이 가능하게 만들기 때문이다.
Contribution
새로운 data relabeling 알고리즘으로 goal conditioned hierarchical policy를 학습하여 IL step에서 완벽하지 않은 policy를 challenging 한 long-horizon task에서 amenable하도록 개선했다.
Hierarchical policy를 학습하기 위해서 structured and segmented demonstration을 준비해야하는 부담을 줄였다.
Related Work
HRL 문제 exploration and optimization
해결점 저자는 additional supervision을 unstructured, unsegmented demonstration을 사용하여 제공한다. 좀더 구체적으로 말하면 reward가 없거나 희소한 RL, large scale generalizable IRL, HRL 의 맥락에서 goal conditioned RL을 사용하여 data 를 relabeling 하는 알고리즘을 사용한다.
HRL 문제
전통적인 HRL 은 demonstration으로 부터 transition segment를 추출하는 것에 초점을 둔다. 그 방법은 IL을 수행하여 low-level의 primitive 나 latent conditioned policy를 학습하여 demonstration으로 부터 의미있는 segment를 만들어낸다. 하지만 그방법은 단순한 imitation이라서 학습된 primitive를 subsequent RL를 가지고 개선해나갈 수 없기 때문에 long-horizon problem에서 challenge가 있다고 한다.
해결점
저자는 imitation과 RL을 둘다 사용하는 방법을 채택했다. individual primitive들을 의미있는 subtask로 explicit하게 분리하는 것 대신에 Relay Reinforcement Fine tuning(RRF) stage에서 Relay Imitation Learning(RIL) stage에서 생성된 Goal conditioned hierarchical policy를 fine tuning 하기 위해서 demonstration을 고정된 길이의 segment로 나누어 data를 relabeling했다.
정리
그래서 저자는 새로운 goal relabeling을 도입했고 bi-level policy를 학습하는데 효용성을 보일 수 있었다.
Preliminary
Goal-conditioned reinforcement learning
multiple task를 수행하려면 goal-conditioned policy를 학습해야한다. 그래서 그 policy를 학습하기 위해서 goal-conditioned reward 의 discounted sum of expectation을 maximize하는 goal-conditioned formulation을 제안했다.
| Goal-conditioned policy : $$\pi(a | s,s_g)$$ |
Goal conditioned formulation : \(\mathbb{E}_{s_{g} \sim \mathcal{G}}[\mathbb{E}_{\pi}\sum_{t=0}^T \gamma^{t}r_{i}(s_{t}, a_{t}, s_{g})]\)
Goal-conditioned imitation learning
demonstration dataset 이 각기다른 goal을 도달하려고하는 sequence를 포함한다고 여기고 objective 가 goal conditioned policy에 대해서 likelihood를 maximize하도록 formulation을 했다.
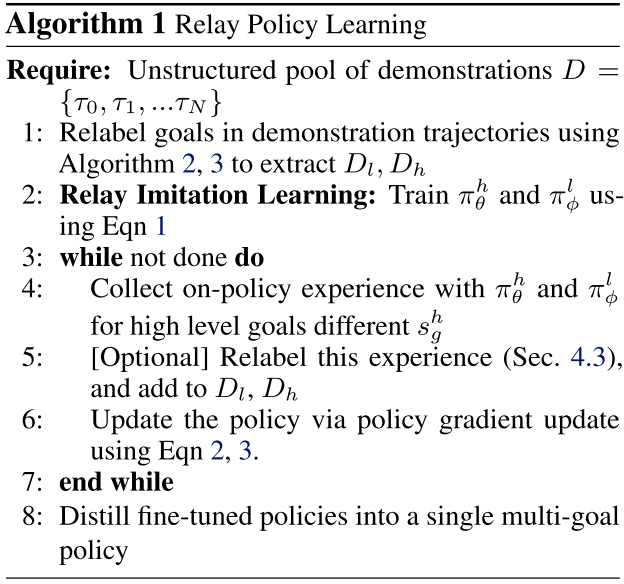
Relay policy Learning
RIL step 만으로는 challenging한 task를 풀 수 없었지만 RRF step을 위한 효과적인 initialization을 제공할 수 있었기 때문에 challenging한(temporally extended) task를 풀 수 있게 됬다.
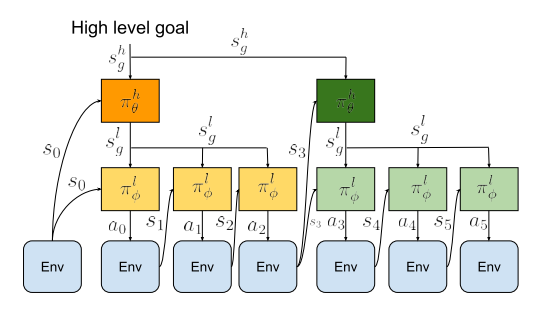
RPL architecture
high-level goal setting policy(setter) $\pi^{h}{\theta}(s^{l}{g}|s,s^{h}_{g})$와 low-level subgoal-conditioned policy $\pi^{l}{\theta}(a|s,s^{l}{g})$로 이루어진 bi-level hierarchical policy를 학습하는 구조이며 이를 통해 high level policy는 low level보다 coarser한 resolution을 제공하기 때문에 temporal abstraction을 가능하게 했다.
high level policy는 high level goal 을 받아서 low level goal을 만들고 이를 다시 resampling하는동안(=고정된 time horizon (H)동안) low level policy는 action을 만들어서 environment에 이행한다.
RIL
기본가정은 test-time goal이 demonstration-time goal과 동일한 분포에서 나와야 한다는 것이다. 그래서 unstructured demonstrationdata를 사용해 policy를 효과적으로 initialization하여 goal relabeling scheme을 세운다. 그로인한 효과는 multi-task generalization 과 compounding error를 handling을 개선할 수 있다는 점이다.
Demondstration은 N개의 Trajectory로 구성되어있고 각 Trajectory는 T길이의 state-action pair이다.
\[D = \{\tau^{i}, \tau^{j}, \tau^{k}, ...\}\] \[\tau^{i} = \{s^{i}_{0},a^{i}_{0},...,s^{i}_{T},a^{i}_{T}\}\]| Demondstration 은 다양한 high-level goal 을 도달하려고 시도하는데 explicit하게 명시하지는 않았다. 대신에 relay data relabeling을 통해 low-level dataset \(D_{l}\)과 high-level dataset \(D_{h}\) 으로 나누어 low level-policy $$ \pi^{l}_{\theta}(a | s,s^{l}{g})\(와 high level-policy\)\pi^{h}{\theta}(s^{l}_{g} | s,s^{h}_{g})$$를 multiple level에서 supervised learning으로 학습한다. |
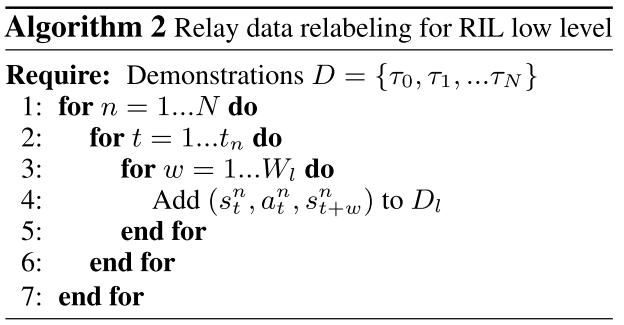
Relay data relabeling for RIL low level
window size \(W_{l}\) 을 고르고 state,goal,action tuple\((s,s^{l}_{g},a)\)을 만들어 Demonstration을 따라 \(W_{l}\) 안에서 goal relabeling하면서 low level dataset \(D_{l}\) 을 구성한다. 핵심은 demonstration에 존재하는 모든 state에서 \(W_{l}\) time step 이내에 state-action pair를 지나 goal에 도달하는 것을 가정으로 하는 점이다. 그렇게하면 \(s_{t+1}, s_{t+2},...,s_{t+W_{l}}\) 를 \(s_{t},...,s_{t+W_{l}-1}\)에서 \(a_{t},...,a_{t+W_{l}-1}\)를 했을 때 도달되는 potential goal 로 여기게 된다.
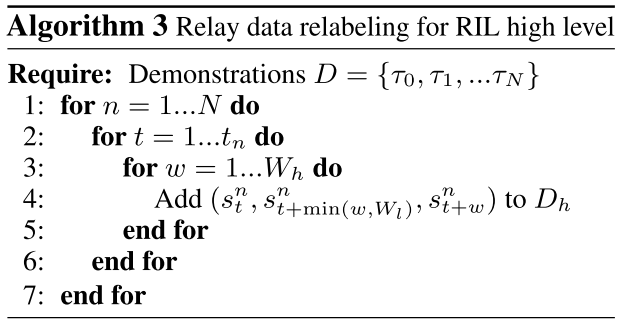
Relay data relabeling for RIL high level
마찬가지로 high level도 window size \(W_{h}\) 를 고르고 state, high-level action(=low-level subgoal), high-level goal tuple \((s, s^{l}_g, s^{h}_g)\)을 만들어 \(D_{h}\)을 구성한다. 즉 \(s_{t+1}, s_{t+2},...,s_{t+W_{h}}\)를 \(s_{t},...,s_{t+W_{h}-1}\)에서 도달가능한 potential high-level goal 로 label울 붙인다. 하지만 high-level action의 경우 충분히 멀리 있는 subgoal을 고르기 위해서 현시점 t로 부터 w step의 goal을 \(s_{t+min(w,W_{l})}\) 로 설정했다.
Objective
| relay-data relabeling을 마친 뒤 low-level과 high-level policy$$\pi^{l}_{\theta}(a | s,s^{l}{g}), \pi^{h}{\theta}(s^{l}_{g} | s,s^{h}_{g})$$ maximize liklelihood의 방법으로 학습한다. Eqn(1) |
이점은 아래와 같다.
- relay-data augmentation 을 통해 더 많은 data generation
- 다양한 목표를 학습하는 것에 의한 generalization
RRF
imitation learning 으로 부터 유래된 compounding error 때문에 temporary extended task 를 잘 수행하지 못했는데 multi-task에서 RIL step으로 initialized된 policy를 fine tuning 함으로써 문제를 해결한다.
bi-level policy를 doubled optimization에서 adaptive step size를 갖는 NPG의 변종인 Goal conditioned HRL알고리즘을 사용하고 그렇게 하기 위해서는 reward function이 필요하고 그것의 sum을 maximize한다.
low-level goal reaching reward function 은 \(r_{l}(s_{t},a_{t},s^{l}_{g})\) 이고 high-level goal reaching reward function 은 \(r_{h}(s_{t},g_{t},s^{h}_{g})\) 이다.
각 objective에 대한 gradient는 아래와 같다. Eqn(2), (3)
/
위의 식은 RRF동안에 off-policy를 적용할 수 있게 해준다고 한다.(???이해잘안감)
policy initialization과 off-policy의 효과를 보여주기 위해 다음과 같은 3가지를 비교했다.
- IRIL-RPL은 off-policy data를 통합한 방식
- DAPG-RPL은 off-policy addition 을 사용하지 않은 방식
- NPG-RPL은 off-policy addition도 사용하지 않고 objective의 두번째항을 포함하지 않아서 policy initialization도 하지 않은 방식
전체 알고리즘은 아래와 같다.
참조에 따르면 high variance와 gradient의 충돌로 on-policy 방법으로 multiple task를 학습시키기가 어렵다고 한다. 그래서 RPL을 사용해서 각각 다른 high level goal에 대해서 fine tuning을 하고 학습된 behavior를 하나의 policy에서 주입하는 방식을 사용한다. 그렇게하면 multi-task optimization의 challenge를 다룰 수 있다.
Experiment
실험내용을 정리하면 다음과 같다.
- unstructured and unlabelled demonstration을 사용한 RIL의 IL 개선여부
- RIL의 RL의 fine tunning에 적합여부
- RPL의 long-horizon task 성공여부
Setup
MuJoCo Enviornment를 사용했다.
kitchen scene이며 구성은 다음과 같다.
- an openable microwave
- four turnable oven burners
- an oven light switch
- a freely movable kettle
- two hinged cabinets
- a sliding cabinet door (slider)
compound goals in the kitchen environment
(a) microwave, kettle, light, slider
(b) kettle, burner, slider, cabinet,
(c) burner, top burner, slide hinge,
(d) kettle, microwave, top burner, lights
PUPPET MuJoCo VR system 을 사용하여 unstructured and unsegmented human demonstration을 얻었다고 한다.
400 sequences 이고 각 sequence는 four different elements 를 갖는다.
Evaluation and Comparisons
각 compound goal을 수행하는 policy를 step completion score를 통해 평가한다.
비교를 위한 baseline 알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
- BC : flat conditioned behavior cloning followed by finetuning
- GCBC : BC에서 data relabelling이 추가 된 것
- DAPG-BC : Rajeswaran이 제안한 loss 로 BC를 finetuning 한것
- DAPG-GCBC : Rajeswaran이 제안한 loss 로 GCBC를 finetuning 한것
- HIL + oracle segmentation scheme을 추가하여 finetuning한 것
- HIRO : Q-learning대신에 NPG 으로 training 한 on-policy 방식
- Nearest Neighbor
1부터4는 BC의 변종들이고 5부터7은 RPL을 비교군이다.
Relay Imitation Learning from Unstructured Demonstrations
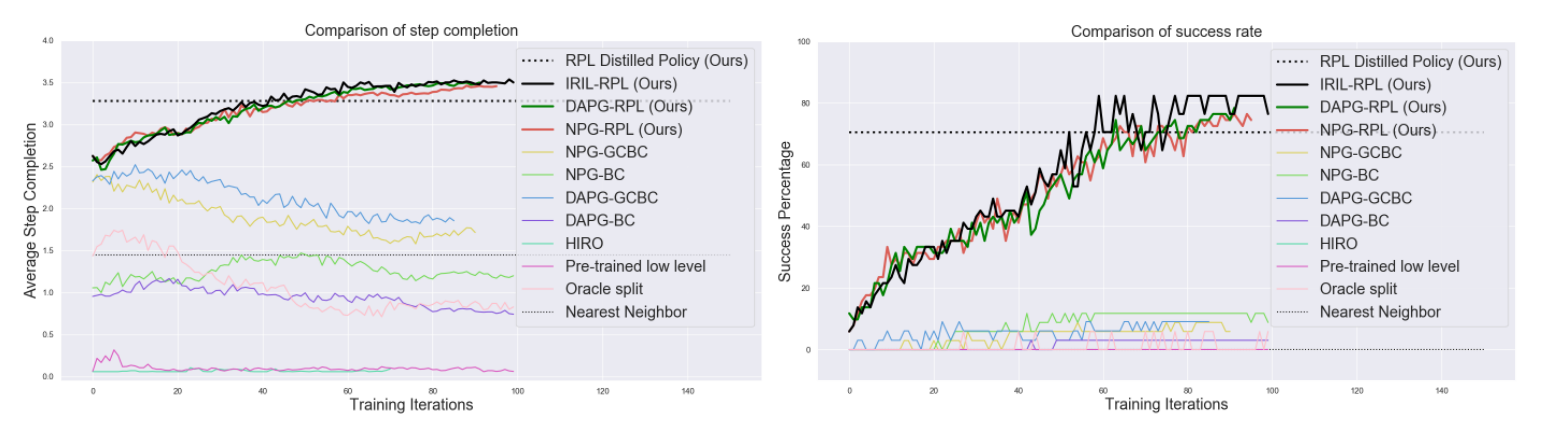
17 개의 서로다른 compound goal에 대해서 step-wise completion scores 를 비교하므로써 RIL이 IL을 개선했다는 것을 보였다.
relabeling의 효과로 소폭 상승이 있었고 Hierarchical structure를 도입했을 때 대폭 상승이 있었다.
Relay Reinforcement Fine-tuning of Imitation Learning Policies
마찬가지로 17 가지 compund goal에 대해서 RIL 만으로는 역시 20퍼센트 정도로 한계를 보였기에 finetuning이 얼마나 효과를 보였는지 비교했다. 실험결과 bi-level에서 fine tuning을 하면 cost가 non-stationary해지기 때문에 low level에만 fine tuning하는 것만으로도 충분하다고 한다.
역시 예상했던대로 NPG-RPL, DAPG-RPL, IRIL-RPL 순서대로 소폭상승을 보였다.
on-policy 방식의 HRL알고리즘(on-policy HIRO)과 비교했을 때 빠르고 높은 성공률을 보였다. relay policy로 fine tuning한 것과 평범한 policy로 fine tuning한 것을 비교했을때 더 나은 fine tuning이 된 것은 sparse한 reward가 얻어지는 것을 완화함으로써 credit assignment and reward specification problem을 해결책임을 보여준다.
segment가 길어질 수록 exploration problem이 점점 challenging 해지는데 Neariest Neighbor를 baseline으로 두어 비교함으로써 closed-loop policy 가 open-loop policy 보다 더 성공률이 높기 때문에 oracle scheme을 사용하는 것의 이점을 보일 수 있었다. (oracle scheme은 closed-loop policy에 사용되는 방식인가???)
제안한 방법의 성공률이 약 80% 정도 되었다.
Ablations and Analysis
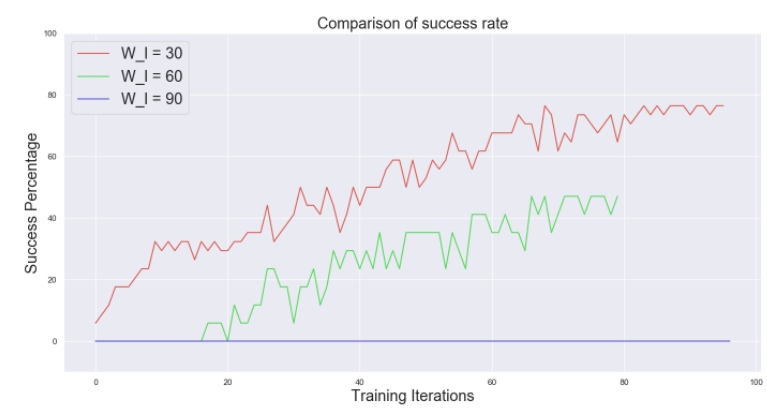
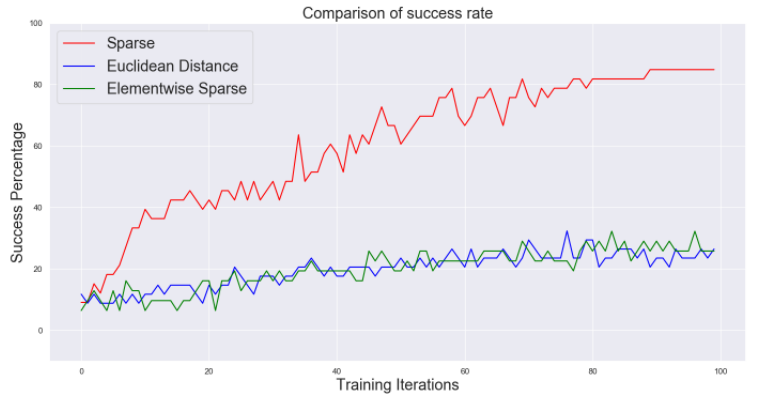
RPL에서 window size의 역할과 reward funtion의 역할을 비교해 보았다.
Behavior가 점점 temporally extended되었기 때문에 window size가 증가할 수록 performance가 떨어진다.
exploration이 충분할 때 sparse한 reward function이 local optima에 빠질 확률이 적어지게 때문에 sparse한 reward function일수록 performance가 증가한다.
Conclusion and Future Work
RPL 을 사용하면 unstructured demonstration을 사용해서 multiple compound goals 을 학습할 수 있는 single policy를 학습 할 수있다.
남아있는 문제는 다음과 같다.
- generalization to longer sequences
- extrapolation beyond the demonstration data
- improvement of data-efficiency
- real world learning

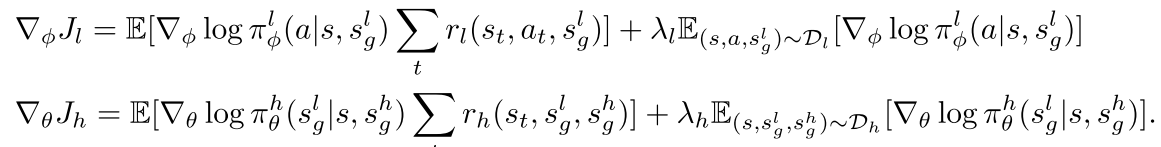


Leave a comment