RRT
Search Space가 연속적이고 고차원인 경우 그리고 주변 영역에 장애물이 많을 때
샘플링 기반 경로 계획 방법이 효율적이다.
아이디어는 랜덤으로 탐색을 하면서 Tree를 확장시켜가면서 경로를 만들자는 방법이다.
Google Colab에 RRT를 Tutorial 식으로 돌려볼 수 있도록 공개되어 있어 빈 부분을 작성하고 돌려보자.
Pseudo Code
우선 알고리즘에 앞서 동작방법을 알아보자.
시작 노드를 root로 설정한다.

난수를 생성시겨서 가장 가까운 노드를 찾고

생성된 난수 방향으로 새로운 노드를 만들고 충돌을 체크하고 충돌하지 않으면 tree로 편입한다.

위 그림은 충돌이 일어났을 때 상황이고 이 경우 새로운 노드를 버리고 다시 위의 과정을 반복한다.
마지막으로 충돌이 일어나지 않았을 때는 목표점에 도달하면 트리가 완성된 것으로 본다.
코드
다시 천천히 코드를 살펴보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
ef plan(self):
"""Plans the path from start to goal while avoiding obstacles"""
self.node_list = [self.start]
for i in range(self.max_iter):
# modify here:
# 1) Create a random node (rnd_node) inside
# the bounded environment
rnd_node = self.get_random_node()
# 2) Find nearest node (nearest_node)
nearest_node = self.get_nearest_node(self.node_list, rnd_node)
# 3) Get new node (new_node) by connecting
# rnd_node and nearest_node. Hint: steer
new_node = self.steer(nearest_node, rnd_node, self.max_extend_length)
# 4) If the path between new_node and the
# nearest node is not in collision, add it to the node_list
if not self.collision(new_node, nearest_node, self.obstacle_list):
self.node_list.append(new_node)
# Don't need to modify beyond here
# If the new_node is very close to the goal, connect it
# directly to the goal and return the final path
if self.dist_to_goal(self.node_list[-1].p) <= self.max_extend_length:
final_node = self.steer(self.node_list[-1], self.goal, self.max_extend_length)
if not self.collision(final_node, self.node_list[-1], self.obstacle_list):
return self.final_path(len(self.node_list) - 1)
return None # cannot find path
위의 코드가 RRT Plan의 핵심 부분이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def final_path(self, goal_ind):
"""Compute the final path from the goal node to the start node"""
path = [self.goal.p]
node = self.node_list[goal_ind]
# modify here: Generate the final path from the goal node to the start node.
# We will check that path[0] == goal and path[-1] == start
while node.parent is not None:
path.append(node.p)
node = node.parent
path.append(node.p)
return path
마지막으로 목표 노드에서 부터 부모를 타고 올라가서 루트 노드까지 올라가면 최종 경로가 완성된다.
결과
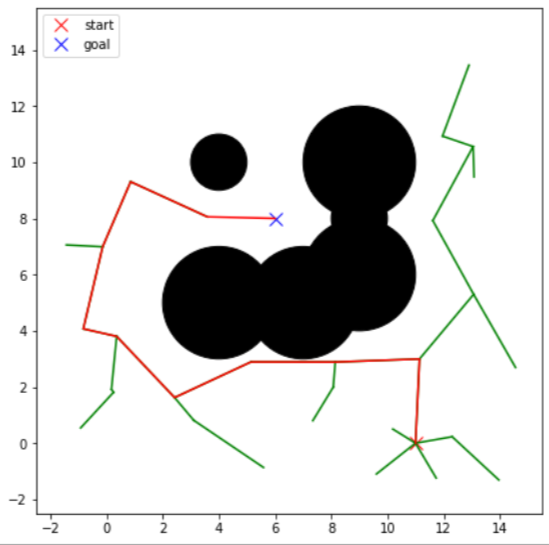
빠른 시간안에 장애물을 회피하며 목표까지 경로를 찾았지만 생성된 경로가 최적 경로는 아니며
경로가 따라가기에 매끄럽지 못해 이동체가 holonomic system 에서만 따라 갈 수 있는 경로이다.
목표까지 도달하기에 Search Space가 매우 큰 경우의 결과를 보자.
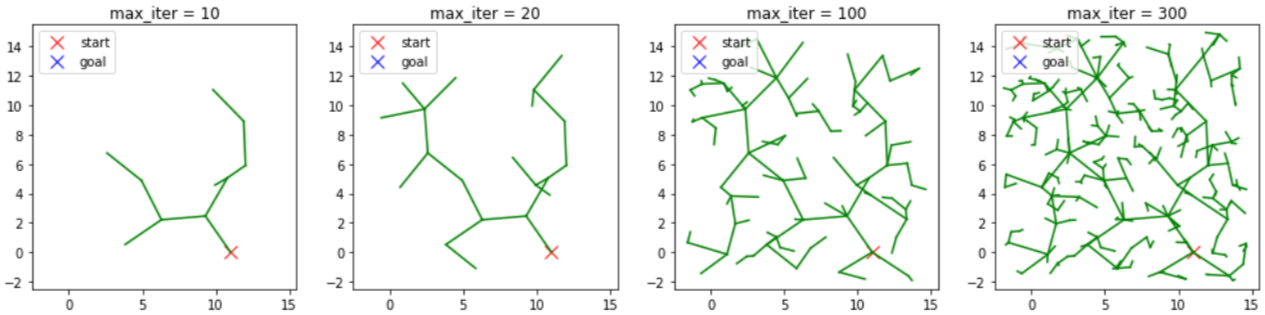
Search에 필요한 난수의 숫자에 따라서 생성된 Tree를 보여준다.
난수가 좁은 영역에만 뿌려진다면 결국 목표에 도달하지 못한다.
즉 최적해를 보장 할 수가 없다.
고찰
RRT알고리즘은 많은 한계점을 갖고 있다.
도착점까지 수렴하는 데 임의로 탐색을 하기 때문에 많은 시간이 소요된다.
장애물이 동적 장애물이라면 매 순간마다 tree를 바꾸지 않는다.
목표지점까지 생성된 경로 자체가 최적이 아니다.
경로가 이동체의 운동학적 특성을 반영하지 않고 오로자 기하학적인 관계만 고려한다는 점도 있다.
실제 적용할 때는 위와 같은 이유들로 목표점까지 길게 경로를 생성하기 어렵다.
그래서 정해진 깊이까지 tree를 만들고 목표와 가까운 지점까지
비용함수를 생성하여 목표 노드를 선택한다.
그리고 생성된 tree를 따라서 목표노드까지 움직이는 경로를 만들어서 움직인다.
다시 새로운 위치에서 tree를 만들고 움직이고를 반복하게 될 것이다.
RRT의 문제를 해결하려면 생성된 tree가 이동체의 운동학적 특성을 반영하여야 하고
최적 경로를 위해서 매순간 rewiring해서 optimal한 path가 되도록 해야할 것이다.
RRT* 나 이후의 많은 방법들은 다룬다.


Leave a comment