In [1]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import deque
from IPython.display import HTML
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
%matplotlib inline
DFS와 BFS의 응용
무한히 큰 Tree에서 특정 깊이까지만 search하고 path를 만들어보자.
Toy Example
Toy Example 을 만들고 bfs와 dfc를 통해 문제를 풀어보자.
In [2]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_nodes_from(np.arange(1,18,1))
pos = nx.circular_layout(G)
nx.add_path(G, [1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
nx.add_path(G, [5,16,17])
nx.add_path(G, [3, 8,9,10,11])
nx.add_path(G, [9,12])
nx.add_path(G, [8,13,14,15])
nx.draw_networkx(G, pos=pos, with_label=True)
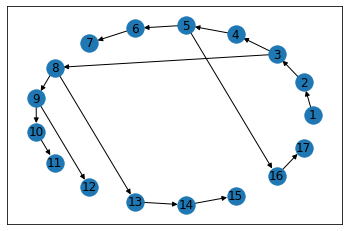
DFS with recursive call
In [3]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
edges = []
def dfs(i, depth, max_depth = 6):
seen = {}
if depth == max_depth:
return
seen[i] = True
print("visit node[{}], depth={}".format(i, depth))
for j in G.adj[i]:
if not j in seen:
if depth < max_depth-1:
edges.append((i,j))
dfs(j, depth + 1)
dfs(i=1, depth=0)
print(edges)
f, axes = plt.subplots()
tree = nx.DiGraph()
# pos = nx.spring_layout(G)
pos = nx.circular_layout(G)
def update(edge):
i,j = edge
tree.add_nodes_from(np.arange(1,18,1))
tree.add_edge(i,j)
plt.cla()
nx.draw_networkx(tree, pos=pos, with_labels=True, width=2.0, alpha=0.8)
grays = set()
for i, j in tree.edges():
grays.add(i)
grays.add(j)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(tree, pos=pos, nodelist=grays, node_color='gray', alpha=0.8)
ani = FuncAnimation(
fig=f, func=update,
frames=edges,
blit=False, interval=1000) # True일 경우 update function에서 artist object를 반환해야 함
HTML(ani.to_html5_video())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
visit node[1], depth=0
visit node[2], depth=1
visit node[3], depth=2
visit node[4], depth=3
visit node[5], depth=4
visit node[6], depth=5
visit node[16], depth=5
visit node[8], depth=3
visit node[9], depth=4
visit node[10], depth=5
visit node[12], depth=5
visit node[13], depth=4
visit node[14], depth=5
[(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (5, 16), (3, 8), (8, 9), (9, 10), (9, 12), (8, 13), (13, 14)]
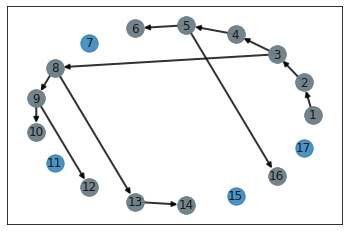
DFS with stack
recursive call 을 사용해서 함수를 구현하면
매우 큰 문제에서 너무많은 recursive call 이 일어났을 때,
recursion error가 발생할 수 있다.
따라서 다음과 같이 stack 자료구조를 통해서
함수안에서 동작하도록 하면 그 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
In [4]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
def dfs(i, max_depth=6):
seen = {}
stack = [(i, 0)]
while stack:
k, depth = stack.pop()
if depth == max_depth:
continue
seen[k] = True
print("visit node[{}], depth={}".format(k, depth))
for j in G.adj[k]:
if j not in seen:
stack.append((j, depth+1))
dfs(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
visit node[1], depth=0
visit node[2], depth=1
visit node[3], depth=2
visit node[8], depth=3
visit node[13], depth=4
visit node[14], depth=5
visit node[9], depth=4
visit node[12], depth=5
visit node[10], depth=5
visit node[4], depth=3
visit node[5], depth=4
visit node[16], depth=5
visit node[6], depth=5
BFS
In [5]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
edges = []
def bfs(i, depth, max_depth = 6):
seen = {}
queue = deque([(i, 0)])
seen[i] = True
while queue:
k, depth = queue.popleft()
if depth == max_depth:
continue
print("visit node[{}], depth={}".format(k, depth))
for j in G.adj[k]:
if not j in seen:
if depth < max_depth - 1:
edges.append((k,j))
seen[j] = True
queue.append((j, depth + 1))
bfs(i=1, depth=0)
print(edges)
f, axes = plt.subplots()
tree = nx.DiGraph()
# pos = nx.spring_layout(G)
pos = nx.circular_layout(G)
def update(edge):
i,j = edge
tree.add_nodes_from(np.arange(1,18,1))
tree.add_edge(i,j)
plt.cla()
nx.draw_networkx(tree, pos=pos, with_labels=True, width=2.0, alpha=0.8)
grays = set()
for i, j in tree.edges():
grays.add(i)
grays.add(j)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(tree, pos=pos, nodelist=grays, node_color='gray', alpha=0.8)
ani = FuncAnimation(
fig=f, func=update,
frames=edges,
blit=False, interval=1000) # True일 경우 update function에서 artist object를 반환해야 함
HTML(ani.to_html5_video())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
visit node[1], depth=0
visit node[2], depth=1
visit node[3], depth=2
visit node[4], depth=3
visit node[8], depth=3
visit node[5], depth=4
visit node[9], depth=4
visit node[13], depth=4
visit node[6], depth=5
visit node[16], depth=5
visit node[10], depth=5
visit node[12], depth=5
visit node[14], depth=5
[(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (3, 8), (4, 5), (8, 9), (8, 13), (5, 6), (5, 16), (9, 10), (9, 12), (13, 14)]
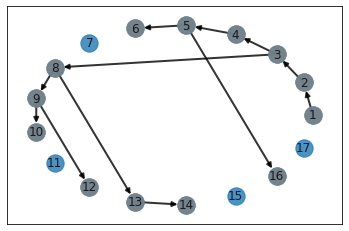
DFS with Recursive call 을 사용한 path생성
stack을 이용하는 경우 매개변수 파라미터는 깊은 복사가 이루어져야 한다.
In [6]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import copy
ans = []
def dfs(i, depth, path:list, max_depth = 6): # type of path should be immutable. if mutable, use deepcopy.
# visit time:
seen = {}
if depth == max_depth:
return
seen[i] = True
print("visit node[{}], depth={}, path={}".format(i, depth, path))
if depth == max_depth - 1:
ans.append(path)
print (ans)
# exploration:
for j in G.adj[i]:
if not j in seen:
path_ = copy.deepcopy(path)
if depth < max_depth - 1:
path_.append(j)
dfs(j, depth + 1, path=copy.deepcopy(path_))
# finish time:
start = 1
dfs(i=start, depth=0, path=[start])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
visit node[1], depth=0, path=[1]
visit node[2], depth=1, path=[1, 2]
visit node[3], depth=2, path=[1, 2, 3]
visit node[4], depth=3, path=[1, 2, 3, 4]
visit node[5], depth=4, path=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
visit node[6], depth=5, path=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]
visit node[16], depth=5, path=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16]]
visit node[8], depth=3, path=[1, 2, 3, 8]
visit node[9], depth=4, path=[1, 2, 3, 8, 9]
visit node[10], depth=5, path=[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10]]
visit node[12], depth=5, path=[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12]]
visit node[13], depth=4, path=[1, 2, 3, 8, 13]
visit node[14], depth=5, path=[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12], [1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14]]
In [7]:
1
ans
1
2
3
4
5
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16],
[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10],
[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12],
[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14]]
DFS with stack 을 사용한 path생성
In [8]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
ans = []
def dfs(i, max_depth=6):
seen = {}
path = [i]
stack = [(i, 0, path)]
while stack:
k, depth, path = stack.pop()
if depth == max_depth:
continue
seen[k] = True
print("visit node[{}], depth={}, path = {}".format(k, depth, path))
if depth == max_depth - 1:
ans.append(path)
print(ans)
for j in G.adj[k]:
if j not in seen:
path_ = copy.deepcopy(path)
if depth < max_depth - 1:
path_.append(j)
stack.append((j, depth+1, path_))
dfs(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
visit node[1], depth=0, path = [1]
visit node[2], depth=1, path = [1, 2]
visit node[3], depth=2, path = [1, 2, 3]
visit node[8], depth=3, path = [1, 2, 3, 8]
visit node[13], depth=4, path = [1, 2, 3, 8, 13]
visit node[14], depth=5, path = [1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14]
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14]]
visit node[9], depth=4, path = [1, 2, 3, 8, 9]
visit node[12], depth=5, path = [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12]
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12]]
visit node[10], depth=5, path = [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10]
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10]]
visit node[4], depth=3, path = [1, 2, 3, 4]
visit node[5], depth=4, path = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
visit node[16], depth=5, path = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16]
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16]]
visit node[6], depth=5, path = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12], [1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]
In [9]:
1
ans
1
2
3
4
5
[[1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 14],
[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 12],
[1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]


Leave a comment