Hidden Markov Model under Continuous Observation
기존의 HMM은 discrete observation에 대해서만 적용이 가능했다. 만약 continous observation에서 HMM을 적용하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
observation을 Gaussian Variable로 모델링하면 된다. 그러면 각 state별로 평균과 분산에 대한 파라미터를 추정한다면 위의 문제를 풀 수 있게된다.
예를 들어, hot/cold state에서 온도를 관측한다고 하자.
관측값은 $P(\mu_{1}, \sigma_{1} \vert hot)$ 과 $P(\mu_{2}, \sigma_{2} \vert cold)$ 의 두 분포중 하나에 속하게 될 것이다.
두 분포의 확률을 각각 방출확률로 추정한다면 discrete observation을 continuous observation으로 확장할 수 있다.
reference
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from hmmlearn.hmm import GaussianHMM
np.set_printoptions(precision=3, suppress=True)
Define Model
1
2
3
4
5
model = GaussianHMM(n_components=2, covariance_type="diag")
model.startprob_ = np.array([0.9, 0.1])
model.transmat_ = np.array([[0.95, 0.05], [0.15, 0.85]])
model.means_ = np.array([[5.0], [-10.0]])
model.covars_ = np.array([[15.0], [40.0]])
Generate Samples
1
2
X, Z = model.sample(1000)
X.shape, Z.shape
1
((1000, 1), (1000,))
Visualize Distribution of Samples
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
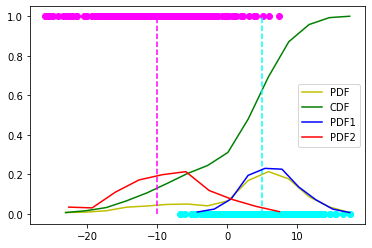
count, bins_count = np.histogram(X, bins=15)
pdf = count / sum(count)
# using numpy np.cumsum to calculate the CDF
# We can also find using the PDF values by looping and adding
cdf = np.cumsum(pdf)
# plotting PDF and CDF
plt.plot(bins_count[1:], pdf, color="y", label="PDF")
plt.plot(bins_count[1:], cdf, color="g", label="CDF")
plt.vlines(x=5, ymin=0, ymax=1.0, color='cyan', ls='--')
plt.vlines(x=-10, ymin=0, ymax=1.0, color='magenta', ls='--')
mask = Z == 0
count, bins_count = np.histogram(X[mask], bins=10)
pdf = count / sum(count)
plt.plot(bins_count[1:], pdf, color="b", label="PDF1")
count, bins_count = np.histogram(X[~mask], bins=10)
pdf = count / sum(count)
plt.plot(bins_count[1:], pdf, color="r", label="PDF2")
plt.scatter(X[mask], Z[mask], color='cyan')
plt.scatter(X[~mask], Z[~mask], color='magenta')
plt.legend()
1
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f018c473e90>
1
2
3
4
5
6
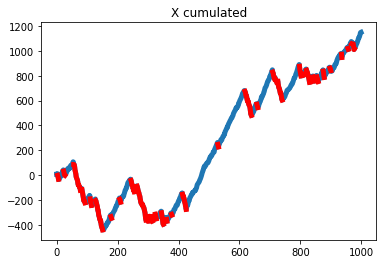
X_cumsum = X.cumsum()
X_cumsum_hat = X_cumsum.copy()
X_cumsum_hat[mask] = np.nan
plt.plot(X_cumsum, lw=5)
plt.plot(X_cumsum_hat, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.title("X cumulated")
1
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'X cumulated')
Train Model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
trained_model = GaussianHMM(n_components=2, n_iter=len(X), verbose=True, tol=1e-10)
print("initial model parameters:\n"
f'startprob : {trained_model.startprob_prior}\n'
f'transmat_: {trained_model.transmat_prior}\n'
f'means: {trained_model.means_prior}\n'
f'covars: {trained_model.covars_prior}\n')
trained_model.fit(X)
print("GT model parameters:\n"
f'startprob : {model.startprob_}\n'
f'transmat_: {model.transmat_}\n'
f'means: {model.means_}\n'
f'covars: {model.covars_}\n')
print("final model parameters:\n"
f'startprob : {trained_model.startprob_}\n'
f'transmat_: {trained_model.transmat_}\n'
f'means: {trained_model.means_}\n'
f'covars: {trained_model.covars_}\n')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
initial model parameters:
startprob : 1.0
transmat_: 1.0
means: 0
covars: 0.01
GT model parameters:
startprob : [0.9 0.1]
transmat_: [[0.95 0.05]
[0.15 0.85]]
means: [[ 5.]
[-10.]]
covars: [[[15.]]
[[40.]]]
final model parameters:
startprob : [1. 0.]
transmat_: [[0.948 0.052]
[0.142 0.858]]
means: [[ 5.174]
[-9.955]]
covars: [[[15.173]]
[[41.75 ]]]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
1 -3668.0490 +nan
2 -3298.6730 +369.3759
3 -3174.2007 +124.4723
4 -3134.2000 +40.0007
5 -3129.1966 +5.0034
6 -3128.6905 +0.5061
7 -3128.6226 +0.0679
8 -3128.6108 +0.0118
9 -3128.6085 +0.0023
10 -3128.6080 +0.0005
11 -3128.6079 +0.0001
12 -3128.6079 +0.0000
13 -3128.6079 +0.0000
14 -3128.6079 +0.0000
15 -3128.6079 +0.0000
16 -3128.6079 +0.0000
17 -3128.6079 +0.0000
18 -3128.6079 +0.0000
19 -3128.6079 +0.0000
20 -3128.6079 +0.0000
21 -3128.6079 +0.0000
Test
1
2
3
4
5
X, Z = model.sample(1000)
Z_hat = trained_model.predict(X)
accuracy = (Z == Z_hat).sum() / len(Z)
accuracy = 1 - accuracy if accuracy < 0.5 else accuracy
print(f'accuracy : {accuracy*100:<.3f} %')
1
2
accuracy : 98.500 %


Leave a comment