Random Walk Tutorial
Introduction
random walk는 stochastic 혹은 random process 로 알려져있다.
시간에 따라서 랜덤하게 움직이는 경로를 모델링 할 때 주로 사용된다.
robotics 분야에서는 랜덤워크를 사용하여 환경에 대한 Policy의 가치를 평가할 때 주로 사용된다.
1
2
3
4
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
1 Dimensional Case
우선 1차원 데이터에 대해서 random walk를 통해서 path를 만들어보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Probability to move up or down
prob = [0.05, 0.95]
# statically defining the starting position
start = 2
positions = [start]
# creating the random points
rr = np.random.random(1000)
downp = rr < prob[0]
upp = rr > prob[1]
for idownp, iupp in zip(downp, upp):
down = idownp
up = iupp
positions.append(positions[-1] - down + up)
# plotting down the graph of the random walk in 1D
plt.plot(positions)
plt.show()
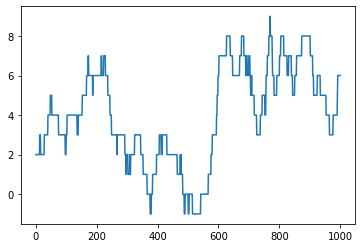
위로갈 확률이 95프로이고 내려갈 확률이 5프로로 이니까
랜덤으로 움직이지만 결국에 전체적으로는 우상향하는 경로가 만들어진다.
2 Dimensional Case
navigation 문제를 풀때 대부분 2D 지도상에 Agent의 정책으로
Random Walk를 사용하여 baseline으로 사용한다.
Random Walk를 통해서 주어진 확률에 대해서 임의의 보행 궤적을 얻을 수 있고
이를 통해서 visitation frequency를 계산 할 수도 있다.
학습을 위한 탐험 정책으로도 주로 사용되며 이를 구현해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# defining the number of steps
n = 10000
# Probability to move right or left or up or down
prob = [0.25, 0.25, 0.28, 0.22]
#creating initial position for containing x and y coordinate
pos = [[0,0]]
for i in range(n):
cur = pos[-1]
val = np.random.choice(range(4), p=prob)
if val == 0:
pos += [[cur[0] + 1, cur[1]]]
elif val == 1:
pos += [[cur[0] - 1, cur[1]]]
elif val == 2:
pos += [[cur[0], cur[1] + 1]]
else:
pos += [[cur[0], cur[1] - 1]]
pos = np.array(pos)
# plotting stuff:
plt.title("Random Walk ($n = " + str(n) + "$ steps)")
plt.scatter(pos[:,0], pos[:,1], s=0.5, c=list(range(n+1)), cmap='coolwarm')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
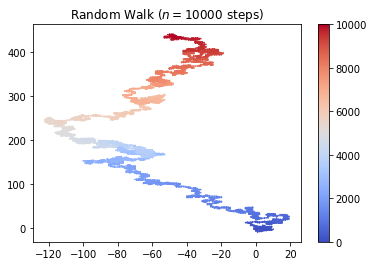
결과를 보면 사전확률이 위쪽으로 가는 것이 조금 더 높기 때문에
random성을 갖지만 시간에 흐름에 따라서 점차 위쪽으로 움직이는 경로가 만들어 지는 것을 볼 수 있다.


Leave a comment